The difference between EPDM with Natural Rubber
2025-08-15

Here’s a concise comparison between **EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)** and **Natural Rubber (NR)** in terms of their properties, applications, and key differences:
---
1. Source & Chemical Structure**

**Why it matters**:
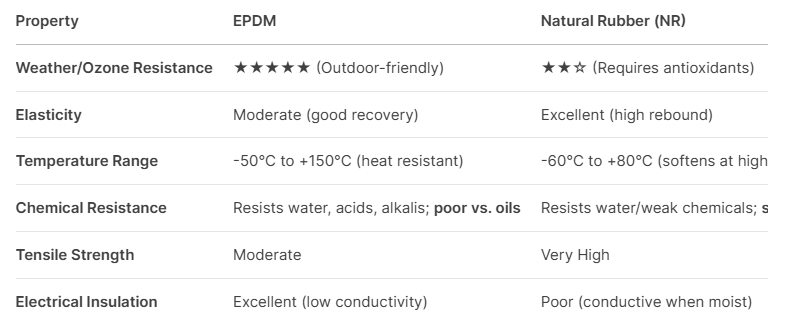
- EPDM’s saturated backbone gives **excellent resistance to oxidation, ozone, and weathering**.
- NR’s double bonds make it **more reactive** (better elasticity but prone to degradation).
---
2. Key Properties**
3. Common Applications**
**EPDM**:
- Automotive weatherstripping, seals (resists UV/ozone).
- Roofing membranes (waterproof, durable).
- Coolant hoses, gaskets (handles heat/steam).
- Electrical insulation (cable coatings).
- **Natural Rubber (NR)**:
- Tires (high grip, low heat buildup).
- Medical gloves, balloons (flexible, biocompatible).
- Vibration dampers, shoe soles (shock absorption).
---
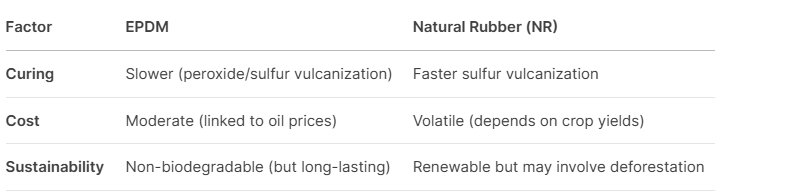
4. Processing & Cost**
-5. Which to Choose?**
- **Pick EPDM if you need**:
- Long-term outdoor use (UV/ozone resistance).
- Heat/chemical resistance (except oils).
- Electrical insulation.
- **Pick Natural Rubber if you need**:
- High elasticity (e.g., tires, dynamic parts).
- Biodegradability or biocompatibility.
- Cost-effectiveness for high-volume uses.
**Quick Summary**
- **EPDM** = Synthetic, weatherproof, heat-resistant, but less elastic.
- **NR** = Natural, super-elastic, biodegradable, but degrades outdoors.
For example:
- **Car door seal?** → EPDM (lasts decades in sun/rain).
- **Surgical glove?** → NR (flexible, safe for skin).
Let me know if you’d like a deeper dive into a specific aspect!
Previous:






