The differences between EPDM and PVC
2025-05-27
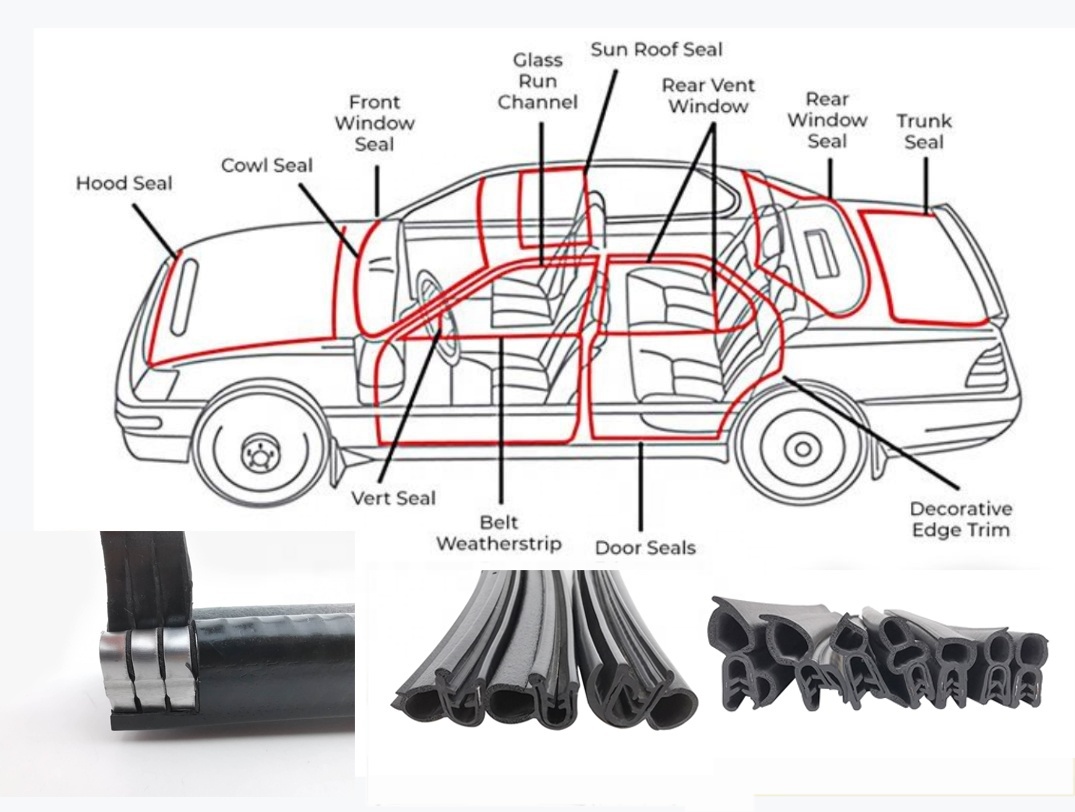
The differences between EPDM and PVC:
Material Composition
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer): A synthetic rubber made from ethylene, propylene, and a small amount of diene monomer.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): A plastic polymer derived from vinyl chloride monomers, often blended with plasticizers.
Flexibility & Durability
EPDM: Highly flexible, weather-resistant, and maintains elasticity in extreme temperatures (-40°C to +120°C).
PVC: Stiffer (unless plasticized), less resistant to temperature fluctuations, and may become brittle over time.
Weather & UV Resistance
EPDM: Excellent UV, ozone, and weather resistance; ideal for outdoor use.
PVC: Prone to degradation under prolonged UV exposure unless stabilized with additives.
Chemical Resistance
EPDM: Resistant to polar solvents, acids, and alkalis but swells in petroleum-based oils.
PVC: Resists oils and fats better but is vulnerable to some solvents and plasticizer migration.
Applications
EPDM: Roofing membranes, automotive seals, gaskets, and outdoor electrical insulation.
PVC: Pipes, window frames, cables, inflatable structures, and synthetic leather.
Environmental Impact
EPDM: More recyclable and environmentally stable.
PVC: Contains chlorine; may release harmful dioxins if burned improperly.
Cost
EPDM: Generally more expensive due to superior durability.
PVC: Cheaper but may require more frequent replacement.
Key Summary: EPDM excels in longevity and extreme conditions, while PVC is cost-effective for rigid or short-term applications.







